Analysis and Modeling
High-accuracy GIS analysis, modeling and mapping for better decision making.
Since its inception, Dougan Ecology has been analyzing geospatial data using cutting edge Geographic Information System (GIS) technology. We are putting tools like LiDAR analysis, and machine learning to the test to better understand, protect, and restore landscapes.

Ecological consultants who leverage the power of GIS and spatial data
We use spatial analysis techniques in almost every project we work on in order to gain insight for decision making, including:
- Mapping constraints and opportunities using policy criteria
- Tree surveys and tree preservation plans
- Designing restoration strategies
- Completing natural asset inventories
- Mapping ecological land classification
- Modeling land cover
- Completing environmental impact assessments
- Delineating feature boundaries
- Identifying significant wildlife habitat
- Conducting municipal natural heritage planning including subwatershed studies
- Predicting current and potential locations for target species including species at risk
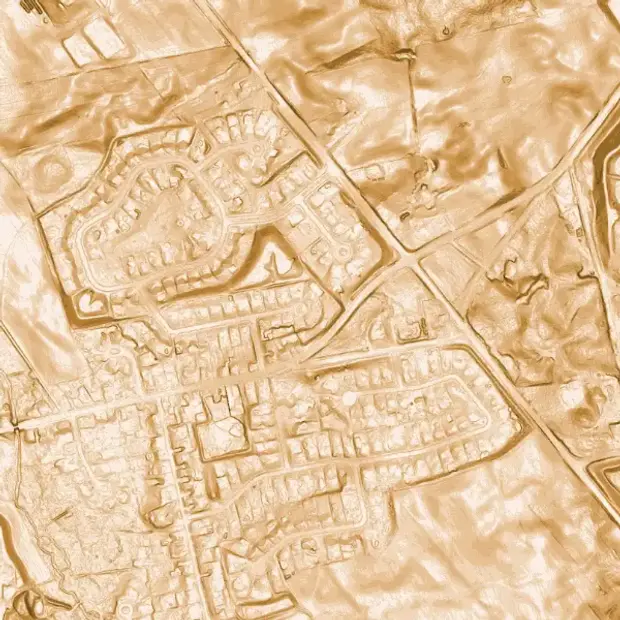

We map land cover, canopy cover, and habitat suitability using custom machine learning tools. We’ve worked on diverse, large-scale projects such as:
- Training deep learning models to predict land cover throughout the Muskoka River Watershed, using orthophotos and LiDAR derivatives
- Using satellite imagery and LiDAR to train deep learning models to map the impacts of hurricane Fiona on urban canopy cover in Charlottetown
We combine ecological expertise with cutting edge technology to deliver maps and geospatial products, and to offer geospatial monitoring and analysis. Our tools include:
- Expert utilization of ESRI’s ArcGIS Pro and ArcGIS Online including Survey123 and FieldMaps for mobile data collection.
- In-house models for mapping the extent of significant wildlife habitat based on provincial ecoregional criteria
- Connectivity modeling to identify probable corridor pathways for animal movement using Linkage Mapper extension for ArcGIS Pro
- Real-time subfoot accuracy for site inventories using a Trimble Catalyst and RTX software
- Data conversion and integration between ArcGIS and AutoCAD platforms
Level up with GIS-powered problem-solving for Ontario and beyond.
You need high-quality information to move your project forward and create a thriving natural environment. We have the integrated team and GIS tools to make it happen.

Frequently asked questions about analysis and modelling
GIS is a powerful tool for understanding and modelling the environment because it allows large amounts of spatial data to be brought together, analyzed, and visualized. We leverage GIS to map natural features such as vegetation communities, canopy cover, and wildlife habitat, and assess how these features interact across the landscape. GIS also supports scenario testing to show how proposed developments, restoration, or climate change could affect ecosystems. By combining science with mapping, GIS helps turn complex environmental data into practical information that supports evidence-based decisions.
Habitat suitability modelling is a process that uses spatial and ecological data to predict where a species is most likely to thrive. It combines information such as vegetation, soils, climate, water availability, and land use to identify areas that provide the right conditions for survival, growth, and reproduction. It supports conservation planning by identifying critical habitats, guiding restoration, and assessing impacts from development or climate change.
Ecological modelling typically integrates data from field surveys, remote sensing, and background records including agency open-source data and citizen science. Combining multiple datasets enhances model accuracy and ensures comprehensive environmental analysis.
Species distribution modelling (SDM) is a method used to predict where a species is likely to occur across a landscape based on environmental conditions and species observations. SDMs combine data on species occurrences with variables such as climate, land cover, topography, soils, and hydrology to identify suitable habitats and estimate the probability of presence. SDM informs conservation prioritization and helps assess risks to species-at-risk in Ontario and Canada.
A habitat suitability model shows where the best conditions exist for a species to live and thrive, based on known habitat characteristics. While a species distribution model predicts where the species is likely to be found based on existing species observations and environmental factors. Both are often used to guide conservation and planning.
Our models help assess the potential impacts of development or land-use changes on ecosystems, supports mitigation planning, and informs regulatory decision-making. By translating complex ecological data into clear, spatially explicit outputs, our models help ensure EIAs are thorough, accurate, and evidence based.
Yes, Dougan Ecology uses spatial and habitat suitability models to predict invasive species’ potential spread, supporting early detection and management efforts.
Landscape connectivity modelling assesses how natural habitats are linked, identifying corridors essential for wildlife movement and genetic exchange, crucial for maintaining biodiversity.
